Pigeon feeds:
The importance of pigeon breeding
Pigeons have been known since ancient times as a delicious and nutritious food due to the high nutritional value. Pigeons have great economic importance, as it picks up the seeds of weeds from the ground, so it helps eliminate them and not spread them between crops. He also picks up grains during the harvest and threshing (as is the case in wheat), so rearing of pigeons in the countryside was to take advantage of the losses in the grain and thus obtain the meat (squab) at the lowest costs.
For the following reasons:
1- pigeons rearing is simpler and easier than raising any other type of poultry, as it does not need night work or industrial spawning, and its chicks do not need specially prepared feed in contrast to chicken chicks, as it is characterized by the fact that it takes care of itself and its chicks, where the male and female collaborate in breeding of its squabs.
2- Pigeon meat (squabs) is one of the finest, tastiest and most delicious types of meat and the easiest to digest, so we find many people prefer it than any other poultry meat.
3- Squabs pigeon becomes prepared for slaughter within a maximum period of 30 days from the date of hatching and is considered the shortest production cycle in comparison to other birds.
4- The high percentage of dressing in the pigeon, where this percentage reaches 75%.
5- Pigeons continue to produce regular production until they are 8-12 years old.
6- Pigeons rarely catch diseases, and from here the pigeons are resistant to many diseases as it is the least infected bird with epidemic diseases, and therefore the mortality rate in the large pigeons and spouses is relatively low compared to poultry.
7- Pigeons are a strong bird that can tolerate weather fluctuations, as they can withstand the summer heat or the cold winter.
8- The small space required for raising pigeons, pigeons can be raised in towers in new land reclamation areas where large areas of legumes and grains are grown.
9- Pigeon waste is one of the most expensive types of organic fertilizers, and the best quality for some crops, such as vegetables, fruits and orchards.
General information about pigeons:
Gender specification:
There are no clear morphological differences between the types of pigeons that determine the features of sex accurately, and the male can be distinguished when his tail is spread out in front of his female to show courtship to her, and he is generally larger in size and has a larger head.
Astigmatism:
Pigeons live in the form of pair couples collectively or individually.
Way of living:
Group or individual, and only one pair can be raised.
the sound:
Pigeons issue a sound called Hadeel “cooing”, and the sound varies in intensity, length, and layers depending on the type of pigeons, its size and age, and there are individual types with specific sounds that are closer to whistling, and the male is the most loud voice.
External characteristics:
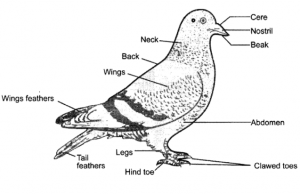
The specifications are variable depending on the quality, the length ranges between 20-40 cm, the color of the eyes varies, as well as the color and shape of the feathers, and some have feathers covering his feet including the toes, and with varying density, the beak has a different shape and length and its colors range from pale black to dark brown, orange yellow and reddish pink. The ability of pigeons to fly varied, as well as its ability to incubate.
Milk of Pigeon:
On the seventh day of the mother or father brood the eggs begins, the appearance of a febrile lobe in the giblets of the fathers increases in growth. On the eighteenth day of brooding (that is, immediately after hatching), the lobule cells begin to form balls or fatty bodies called pigeon milk that disappear after seven days. The main component of pigeon milk is protein, where more than half of the components of pigeon milk are based on dry matter. It also contains most of the essential and non-essential amino acids. The fat is about a third and the rest is ash.
Composition of pigeon milk:
| Ash | Fat | Protein | water |
| 1.6 % | 10% | 16% | 72% |
Squabs feeding system:

Parents feeding the squabs with the milk of the pigeon as it moves from the parent’s giblets to the giblets of squabs. The process of filling the squab’s gland takes a very short time, as it is noticed that the young are so voracious that the giblets of the squabs are very large relative to the rest of the body. As a result of feeding on pigeon milk, body weight doubles several times at the end of the first week.
The feeding process continues pigeons’ milk only for a period ranging between 3 – 4 days from hatching, where the squabs at this age have weak bodies and are unable to benefit from the grains. At the beginning of the fourth day of the life of squabs, parents begin to give the squabs a small percentage of the grains partially digested by the parents ’giblets, and mix them with the milk of the pigeons until the seventh day of the life of squabs. Then, the parents start feeding them on fodder and grains.
Because the increasing of pigeon’s importance in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, AIMCO prepared a number of pigeon diets that are appropriate to the production conditions and its purpose as follows:
AIMCO Pigeon feed 11% Protein:
It is used to cover basic requirements of protein, energy, mineral elements and vitamins.
| Crude protein % | Energy, kcal / kg diet |
|---|---|
| 11 | 2700 |
AIMCO Pigeon feed 13% Protein:
It is used with medium production birds and is balanced in terms of their mineral and vitamins content and covers protein and energy requirements.
| Crude protein % | Energy, kcal / kg diet |
|---|---|
| 13 | 3000 |
AIMCO Pigeon feed 17% Protein:
This formula is used with high-yielding birds, especially when the squabs start feeding.
| Crude protein % | Energy, kcal / kg diet |
|---|---|
| 17 | 3000 |
AIMCO Pigeon feed 18% Protein super formula:
This formula is specific to pigeon with a high growth rate and it differs from others in its high content of mineral elements, vitamins, amino acids, immune stimulants and growth promoters.
| Crude protein % | Energy, kcal / kg diet |
|---|---|
| 18 | 3000 |
| Vitamins | |
| A: 15000 IU / kg, D3: 3750 IU / kg, E: 30 mg / kg, 3K: 4.5 mg / kg, B: 1: 3 mg / kg, B2: 7.5 mg / kg, B3: 60 mg / kg, B5: 18 mg / kg, B6: 7.5 mg / kg, biotin: 0.075 mg / kg, B9: 1.125 mg / kg, B12: 0.0225 mg / kg, C: 150 mg / kg, antioxidant: 0.1875 mg / kg . | |
| Mineral salts: | |
| Manganese: 70 mg / kg, zinc: 60 mg / kg, iron: 60 mg / kg, cobalt: 0.15 mg / kg, copper: 8 mg / kg, iodine: 1 mg / kg, selenium: 0.25 mg / kg | |
AIMCO Pigeon feed 21% Protein:
This formula can be used with the pigeons in the first stage of the squabs breeding.
| Crude protein % | Energy, kcal / kg diet |
|---|---|
| 21 | 2950 |
AIMCO Pigeon feed 24% Protein super formula:
This formula, like the composition of 18%, is characterized by a high content of vitamins, mineral elements, amino acids, growth stimulants and can be used in fattening and with high temperatures as the feed consumed by birds decreases
| Crude protein % | Energy, kcal / kg diet |
|---|---|
| 24 | 3000 |
| Vitamins | |
| A: 15000 IU / kg, D3: 3750 IU / kg, E: 30 mg / kg, 3K: 4.5 mg / kg, B: 1: 3 mg / kg, B2: 7.5 mg / kg, B3: 60 mg / kg, B5: 18 mg / kg, B6: 7.5 mg / kg, biotin: 0.075 mg / kg, B9: 1.125 mg / kg, B12: 0.0225 mg / kg, C: 150 mg / kg, antioxidant: 0.1875 mg / kg . | |
| Mineral salts: | |
| manganese: 91 mg / kg, zinc: 78 mg / kg, iron: 78 mg / kg, cobalt: 0.195 mg / kg, copper: 10.4 mg / kg, iodine: 1.3 mg / kg, selenium: 0.325 mg / kg. | |

